Creative Proteomics has rich experience in the identification of protein post-translational modifications. With a professional team and advanced mass spectrometry facilities, we can provide you with a one-stop protein AMPylation identification service from experimental design to result in delivery, accelerating your research progress.
Protein AMPylation, catalyzed by AMPylator, stably and reversibly adds adenylate 5'-monophosphate (AMP) covalently to the hydroxyl group of protein side chains, resulting in modified proteins with altered activities and the production of proteins, peptides or amino acids. Unstable intermediates allow thermodynamically unfavorable reactions to occur. AMPylation is a post-translational modification that was discovered in the 1960s, also known as adenylation. As AMPylation is an important mechanism for several bacterial infections, including Haemophilus parasitics, the research enthusiasm for AMPylation has been revived.
Service Content of Protein AMPylation Identification
In the protein AMPylation identification service, Creative Proteomics utilizes advanced mass spectrometry facilities to identify adenylated proteins and modification sites of Thr, Ser and Tyr residues. However, MS-based identification of AMPylated sites in living cells is limited by the degree of endogenous modification, making site detection in proteins with low AMP abundance more difficult. In this service, we utilize stable isotope-labeled ATP to address detection limit challenges. The transfer of ATP isotopes to target proteins in crude cell lysates by in vitro AMPylation introduces specific reporter ion clusters, a method that allows us to identify AMPylation in complex biological samples by MS. At the same time, we can also use biotin to identify AMPylation modification sites by MS/MS.
Mass Spectrometry Facilities and Projects
- Q-Exactive and QTOF Mass Spectrometers with MS/MS Capabilities
- Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap Fusion™ Tribrid™ Mass Spectrometer
- Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap Fusion™ Lumos™ Tribrid™ Mass Spectrometer
- Thermo Scientific™ Q Exactive™ HF Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer
Requirements for Samples
- Solution (target protein): total target protein > 50 μg, target protein concentration > 80%.
- Solution (large-scale mixed protein): total protein > 1 mg, protein concentration > 1 μg/μL.
- Please store all samples at -80°C, do not freeze and thaw samples repeatedly, and use sufficient dry ice for transportation.
- Please provide the specific concentration, volume, preparation time, and source of each sample. And inform the sample information as well as the control and experimental samples (if there is a group, describe the group information in detail.)
Deliverables
- Experimental steps
- Relevant mass spectrometry parameters
- Details of the identified phosphorylation sites
- Mass spectrometry images
- Raw data
Our Advantages
- Efficient and professional protein AMPylation identification service.
- Capable of analyzing complex biological samples of various eukaryotes and bacteria.
- Help you explore the important physiological functions of protein AMPylation.
Service Process
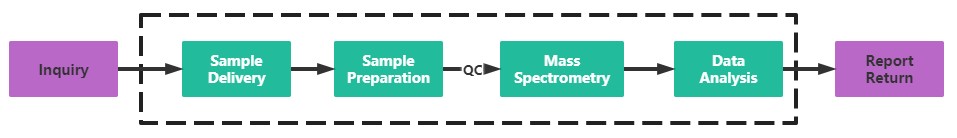
Creative Proteomics has built a mature mass spectrometry detection platform, and our professional mass spectrometry identification team can quickly and accurately solve the problem of protein AMPylation identification for you. If you are interested in our protein AMPylation identification service, please contact us today for technical support.
References
- Rauh, T.; et al. MS-Based in Situ Proteomics Reveals AMPylation of Host Proteins during Bacterial Infection. ACS Infect Dis. 2020, 6(12): 3277-3289.
- Kielkowski, P.; et al. FICD activity and AMPylation remodelling modulate human neurogenesis. Nat Commun. 2020, 11(1): 517.
- Pieles, K.; et al. An experimental strategy for the identification of AMPylation targets from complex protein samples. Proteomics. 2014, 14(9): 1048-1052.
- Woolery, A. R.; et al. AMPylation: Something Old is New Again. Front Microbiol. 2010, 1: 113.
The service is for research only, not for clinical use.