Post-translational modification of proteins is of great significance to life activities. Post-translational modifications of proteins mainly increase the function of proteins through the covalent addition of proteins, the addition of functional groups, and proteolytic cleavage of regulatory subunits. Translationally modified proteins play a huge role in gene expression, signal transmission, and physiological processes. Creative Proteomics has built an internationally recognized mass spectrometry platform and has a strong technical service team, which can provide excellent analysis and identification services for researchers and teams engaged in the identification of protein post-translational modification sites.
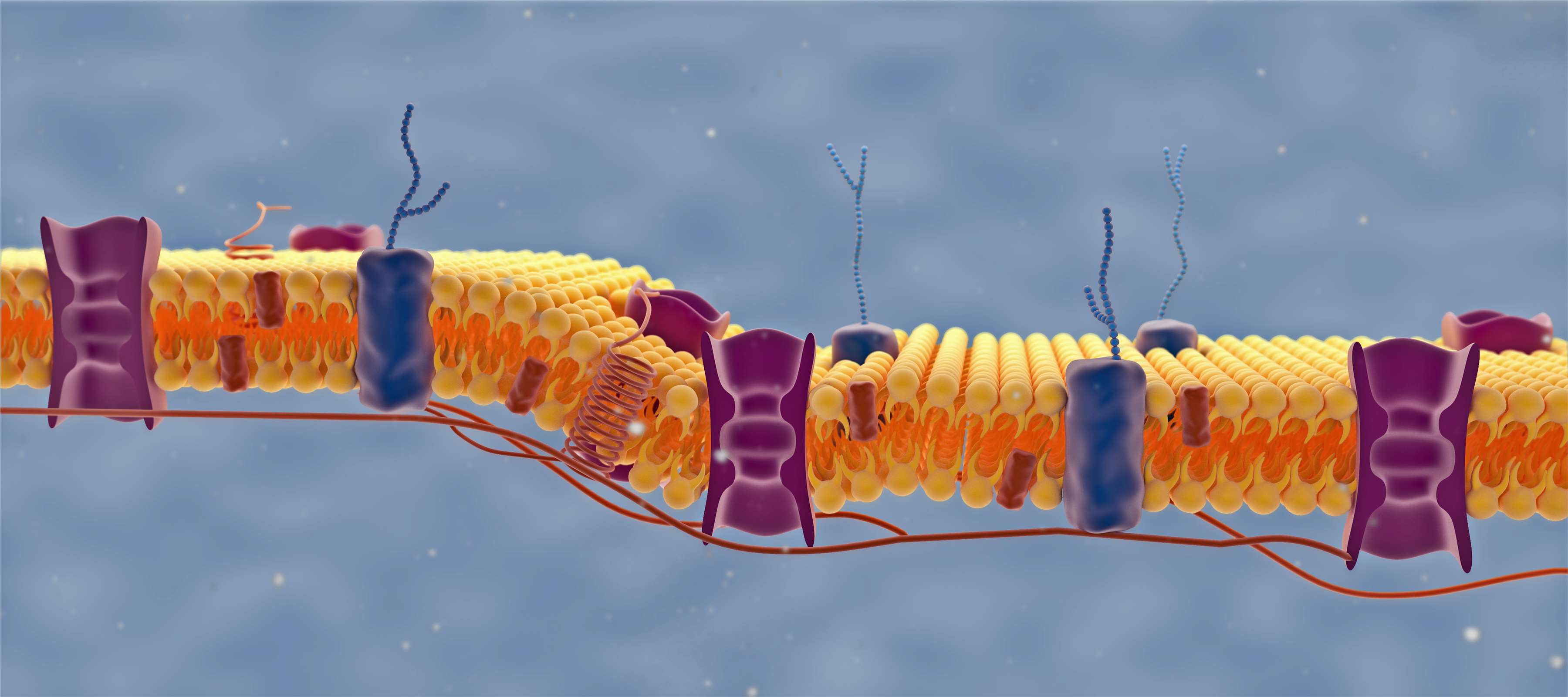
In the process of protein post-translational modification site identification and analysis service, the processed protein samples will be cut into small peptide fragments by enzymes, and then enter the mass spectrometry facility for analysis. The molecular mass information of a series of small peptide fragments is obtained by mass spectrometry. In the absence of any post-translational modification, the sequence information and molecular weight of a particular peptide are determined, but after some post-translational modification occurs, the molecular weight of a certain group will be increased.
The protein post-translational modification identification service can help researchers quickly identify different protein modifications, including phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, nitrosylation, methylation, acetylation, lipidation, and proteolysis. It provides a basis for research in cell biology, disease diagnosis, and disease prevention.
The services we can provide are as follows.
We provide professional protein enrichment services to increase the abundance of phosphorylated proteins. Using mass spectrometry facilities to identify protein phosphorylation sites and degrees of phosphorylation, reveal all the processes of cell proliferation, development, differentiation, apoptosis, and other life activities.
We identify ubiquitinated proteins after trypsin digestion, which can explain various physiological activities such as protein degradation, DNA damage repair, gene transcription, and apoptosis.
This service uses co-immunoprecipitation technology to rapidly and efficiently enrich acetylated peptide fragments, and then uses mass spectrometry facilities to complete the identification, which can effectively analyze the activation of transcriptional regulators in the nucleus, the regulation of metabolic pathways and metabolic enzyme activities, etc. life activity.
We first digested the protein samples, and then used mass spectrometry to identify two major glycoproteins, N-glycoproteins and O-glycoproteins, search for glycosylation sites, and analyze the structure of sugar chains.
We first screened out the peptides of the target protein by primary mass spectrometry, then collected all fragmented signals of the target peptide by secondary mass spectrometry, and finally completed the quantitative analysis of ADP ribosylation-modified proteins by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and other methods.
We can detect citrullination of proteins based on an increase or decrease in monoisotopic mass in mass spectrometry data. 4-Bromophenylglyoxal can also be used to selectively label citrulline polypeptides, and then MALDI-MS analysis can be used to detect protein citrullination.
Our detection service identifies proline hydroxylation of proteins by LC-MS/MS and HPLC/MS to help researchers understand various physiological activities such as animal cell proliferation and plant growth and development.
Our assay service utilizes a variety of mass spectra such as LC-MS to identify adenylated proteins and Thr, Ser, and Tyr residue modification sites, even in complex biological samples with rapid identification of AMPylation.
We use phosphine reagents to directly label SNO for MS analysis, or selectively target and convert labile SNO to stable biotin conjugates for analysis by MS, which can help understand the potential molecules for protein function regulation mechanism.
We first performed reductive alkylation of free sulfhydryl groups by NEM, followed by blocking broken disulfide bonds with IAM, enzymatic separation of substrates in gel or solution, and finally obtained the disulfide bond using advanced mass spectrometry facilities. Full structural information.
Our advanced MALDI-MS or ESI-MS mass spectrometry facilities can quickly identify various inhibitor binding sites, clarify the structural properties of inhibitor binding regions, and provide a theoretical basis for drug development.
We combine various mass spectrometry techniques such as liquid chromatography (LC), electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-ToF-MS), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to complete the formation of adduct sites between mercury and proteins such as hemoglobin point identification.
Creative Proteomics, a leader in mass spectrometry-based analysis services, can provide you with comprehensive and customizable posttranslational modification site identification services. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us .
The service is for research only, not for clinical use.