Creative Proteomics has rich experience in protein post-translational modification identification. With a professional team and advanced mass spectrometry facilities, we can provide you with a one-stop protein S-nitrosation identification service from experimental design to result in delivery to accelerate your research progress.
S-nitrosation, also known as S-nitrosylation, is a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-independent NO signal transduction pathway. It is a reversible reaction based on an intracellular redox state, independent of enzymes but dependent on NO concentration. Whether a protein can be S-nitrosated depends on the amino acid composition at both ends of the cysteine residue and the spatial structure of the protein. S-nitrosation changes protein function by adding NO to cysteine residues of proteins. The functional changes after protein S-nitrosation include enhancing or inhibiting the activity of proteases, changing the transport and subcellular localization of proteins in cells, etc.
Service Content of Protein S-Nitrosation Identification
In the protein S-nitrosation identification service, Creative Proteomics uses advanced mass spectrometry facilities to identify and analyze the nitrosation of proteins. Site-specific identification of SNO proteins is critical for understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms of protein function regulation and for drug development. In this service, we can directly label SNO with phosphine reagents for MS analysis, or selectively target and convert labile SNO to stable biotin conjugates for analysis by MS. We were also able to perform S-nitrosation identification using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after a series of treatments of the samples with CysNO, selective reduction, and iodoTMT six-fold reagents.
Mass Spectrometry Facilities and Projects
- Electrospray-Tandem MS by Triple Quadrupole (ESI-TSQ LC/MS/MS)
- Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap Fusion™ Tribrid™ Mass Spectrometer
- Thermo Scientific™ Orbitrap Fusion™ Lumos™ Tribrid™ Mass Spectrometer
- Thermo Scientific™ Q Exactive™ HF Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer
- Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
Requirements for Samples
- Solution (target protein): total target protein > 50 μg, target protein concentration > 80%.
- Solution (large-scale mixed protein): total protein > 1 mg, protein concentration > 1 μg/μL.
- Please store all samples at -80°C, do not freeze and thaw samples repeatedly, and use sufficient dry ice for transportation.
- Please provide the specific concentration, volume, preparation time, and source of each sample. And inform the sample information as well as the control and experimental samples (if there is a group, describe the group information in detail.)
Deliverables
- Experimental steps
- Relevant mass spectrometry parameters
- Details of the identified phosphorylation sites
- Mass spectrometry images
- Raw data
Our Advantages
- Enables accurate detection and isolation of SNO proteins from cell extracts.
- Help researchers delve deeper into diseases related to the nervous system.
- A high-resolution mass spectrometer enables the detection of specific modification sites and peptides with high precision and accuracy.
Service Process
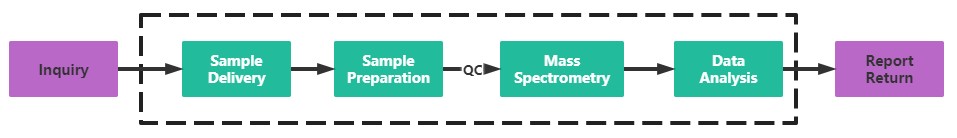
Creative Proteomics has built a mature mass spectrometry detection platform, and our professional mass spectrometry identification team can quickly and accurately solve the problem of protein S-nitrosation identification for you. If you are interested in our protein S-nitrosation identification services, please contact us today for technical support.
References
- Wang, H.; Xian M. Chemical methods to detect S-nitrosation. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011, 15(1): 32-37.
- Thomas, D. D.; Jourd'heuil, D. S-nitrosation: current concepts and new developments. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012, 17(7): 934-936.
- Ye, H.; et al. Protein S-Nitrosation: Biochemistry, Identification, Molecular Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Applications. J Med Chem. 2022, 65(8): 5902-5925.
The service is for research only, not for clinical use.