Creative Proteomics has rich experience in protein post-translational modification analysis. With a professional team and advanced mass spectrometry facilities, we can provide you with a one-stop protein chemical adduct site determination service from experimental design to result in delivery to speed up your research progress.
An adduct is a product formed by direct addition reactions (both electrophilic and nucleophilic types) of two or more reactants with multiple bonds, and it can be considered as a single product formed by a direct combination of different molecules composed of atoms of all reactant molecules. Adducts are usually formed between Lewis acids and Lewis bases. Many biologically active intermediates can form stable adducts with target proteins through electrophilic addition reactions. Such covalent protein modifications can initiate processes that lead to acute tissue damage or chronic disease. The identification of adduct sites contributes to a better understanding of how specific classes of electrophiles generate toxicity and disease progression through site-selective protein-specific covalent modification.
Service Content of Chemical Adduct Site Determination
Mass spectrometry and bioinformatics analysis can help us to study the site-specific modification of proteins by adducts in more detail. In the chemical adduct site determination service, Creative Proteomics is able to use MS to identify the active site serine adduct percentage of biomarker proteins such as serine hydrolase, albumin, tubulin, and transferrin. The sites where mercury forms adduct with proteins such as hemoglobin can be identified by combining liquid chromatography (LC) with ESI-TOF-MS and inductively ICP-MS. Fourier transform mass spectrometry (FT-MS) was also able to identify unique fragments in the adduct digest to locate the primary binding site of cisplatin.
Mass Spectrometry Facilities and Projects
- Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry (FT-MS)
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
- The BioTOF II Electrospray Ionization Time-of-Flight (ESI-TOF) Mass Spectrometer
- Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
Requirements for Samples
- Solution (target protein): total target protein > 50 μg, target protein concentration > 80%.
- Solution (large-scale mixed protein): total protein > 1 mg, protein concentration > 1 μg/μL.
- Please note that for plasma samples use EDTA solution to prevent coagulation. And store all samples at -80°C, do not freeze and thaw samples repeatedly, and use sufficient dry ice for transportation.
- Please provide the specific concentration, volume, preparation time, and source of each sample. And inform the sample information as well as the control and experimental samples (if there is a group, describe the group information in detail.)
Deliverables
- Experimental steps
- Relevant mass spectrometry parameters
- Details of the identified phosphorylation sites
- Mass spectrometry images
- Raw data
Our Advantages
- It can help researchers explore the impact of adduct modification on protein function.
- Can provide customized chemical adduct site determination service according to your needs.
- Chemical adduct sites can be identified using high-resolution mass spectrometry instruments and a variety of methods.
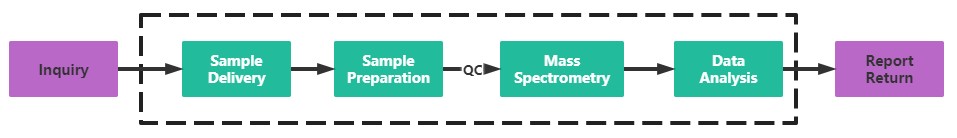
Service Process
Creative Proteomics has long been committed to protein post-translational modification analysis, providing you with various modification identification services. With our professional team and advanced mass spectrometry facilities, we can solve the problem of chemical adduct site determination for you. If you are interested in our chemical adduct site determination service, please contact us today for technical support.
References
- Fisher, A. A.; et al. Utilization of LC-MS/MS analyses to identify site-specific chemical protein adducts in vitro. Methods Mol Biol. 2011, 691: 317-326.
- Marsillach, J.; et al. Protein adducts as biomarkers of exposure to organophosphorus compounds. Toxicology. 2013, 307: 46-54.
- Hogeback, J.; et al. Investigating the adduct formation of organic mercury species with carbonic anhydrase and hemoglobin from human red blood cell hemolysate by means of LC/ESI-TOF-MS and LC/ICP-MS. Metallomics. 2016, 8(1): 101-107.
- Zhao, T.; King FL. Direct determination of the primary binding site of cisplatin on cytochrome C by mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20(6): 1141-1147.
The service is for research only, not for clinical use.